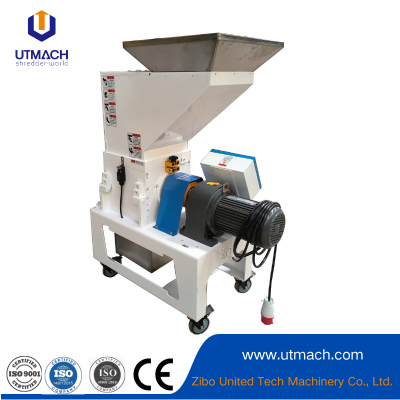
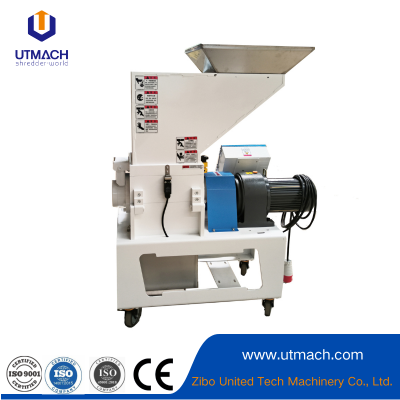
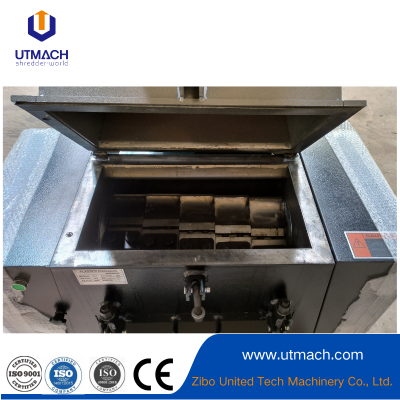
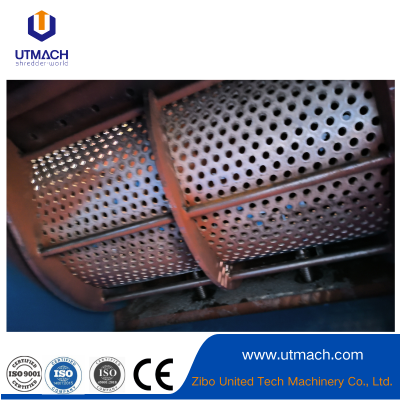
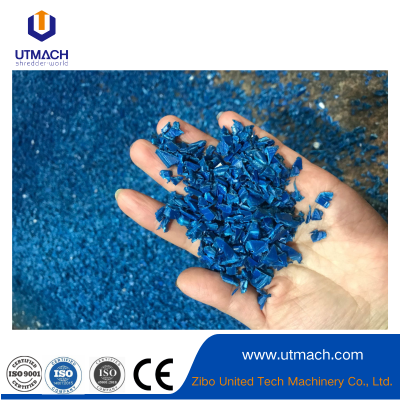
Precision Pellet-forming and Consistent-output Plastic Granulator

A granulator or pelletizer is a specialized machine designed to convert powdery, flaky, or viscous materials into uniform, spherical or cylindrical particles (granules or pellets) through processes like compression, extrusion, or agglomeration. Below is a comprehensive overview of its key aspects:
1. Types of Granulators
Extrusion-Type Pelletizer:
Uses screw-driven extrusion to melt/soften material, which is then cut into pellets.
Common in plastics, chemicals, and food industries.
Roller-Type Granulator:
Relies on rotating rollers to compact powder into sheets, which are crumbled into granules.
Suitable for pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals.
Compression Granulator:
Presses powder into dense granules using rollers or hydraulic pressure.
Often used for brittle materials like coal or fertilizers.
Spray Granulator:
Atomizes liquid onto a moving bed of powder, forming granules through layering.
Used in pharmaceuticals and detergent production.
2. Key Components
Feed System: Delivers raw material (powder, molten plastic, etc.) into the machine.
Screw/Barrel (for Extrusion): Heats and conveys material under pressure.
Die/Nozzle: Shapes extruded material into specific pellet sizes.
Cutting Mechanism: Cuts extruded strips into pellets (e.g., rotary knives).
Cooling System: Rapidly cools pellets to solidify them.
Control Panel: Automates parameters like temperature, speed, and pressure.
3. Working Principle
Material Feeding: Raw material is fed into the hopper.
Processing:
Extrusion: Screw heats/melts material, forcing it through a die.
Compression: Rollers press powder into compacted sheets.
Agglomeration: Liquid binder bonds fine particles into larger granules.
Shaping & Cooling: Extruded material is cut into pellets and cooled.
Output: Uniform granules/pellets are collected for further use.
4. Applications
Plastics Industry: Recycles plastic waste into reusable pellets.
Pharmaceuticals: Forms tablet-ready granules from active ingredients.
Chemicals & Fertilizers: Produces uniform pellets for easy handling/storage.
Food Industry: Pelletizes powders (e.g., milk, spices) for packaging.
Biomass Energy: Compacts wood/straw into biofuel pellets.
5. Key Features
Precision Control: Adjustable speed, temperature, and pressure for consistent output.
High Capacity: Suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Material Versatility: Can process plastics, metals, ceramics, and organic materials.
Energy Efficiency: Modern designs minimize power consumption.
Safety Systems: Overload protection, emergency stops, and dust extraction.
6. Technological Advancements
Automation: PLC/HMI systems for real-time monitoring and adjustment.
Twin-Screw Extruders: Improve mixing efficiency for complex formulations.
Underwater Pelleting: Cools pellets instantly for higher throughput.
Sustainability: Energy recovery systems and low-emission designs.
7. Maintenance & Safety
Regular Cleaning: Prevent material buildup, especially in food/pharma applications.
Component Inspection: Check screws, rollers, and dies for wear.
Safety Protocols: Lockout/tagout procedures, dust masks, and thermal protection.
8. Terminology
Granulation: Process of forming particles from powder.
Pelletizing: Extrusion-based method for plastics/chemicals.
Agglomeration: Particle growth via liquid or heat bonding.
Spheronitizing: Rounding particles for better flow/handling.

Send Inquiry to This Supplier
You May Also Like
-
Non-stop Continuous and Precision Pellet-forming Plastic GranulatorNegotiableMOQ: 1 Set
-
Supercritical-processed and Fully-automated Plastic GranulatorNegotiableMOQ: 1 Set
-
Recyclate-specialized and Modular-designed Plastic GranulatorNegotiableMOQ: 1 Set
-
Clean-production and Precision Controlled Plastic GranulatorNegotiableMOQ: 1 Set
-
Intelligently Temperature-controlled and Wear-resistant Lined Plastic GranulatorNegotiableMOQ: 1 Set
-
Modular-designed and Recyclate-specialized Plastic GranulatorNegotiableMOQ: 1 Set
-
Heat-sensitive Optimized and Recipe-storing Plastic GranulatorNegotiableMOQ: 1 Set
-
Multi-functional and Low-maintenance Plastic GranulatorNegotiableMOQ: 1 Set
-
Corrosion-resistant and High-capacity Plastic GranulatorNegotiableMOQ: 1 Set
-
Environmentally-friendly and Customizable Industrial-grade Plastic GranulatorNegotiableMOQ: 1 Set