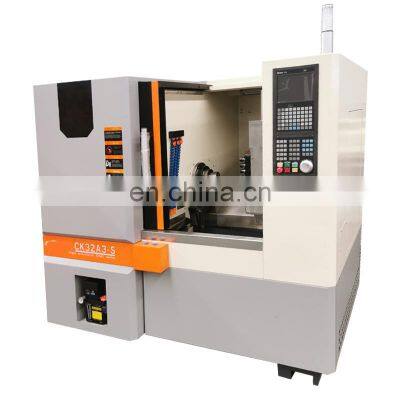
Cnc Machine Lathe Mill Insights & Buyer's Guide
In contemporary industry, precision is critical. Among the different types of machine tools, CNC lathes and CNC mills are the most modern. They offer high precision and efficiency in the machining operations. If you are in the metalworking, woodworking, or any business that requires accurate shaping and cutting, knowing what CNC machines can do is important for your business.
What is a CNC Lathe and How Does It Work?
Understanding the Basics of a CNC Lathe Machine
The CNC lathe machine is categorized as a more advanced instrument used for the exact crafting of cylindrical workpieces. Unlike traditional machines, CNC lathe machines are fully automated and operated with computer software, resulting in a greater level of precision and redundancy. A workpiece is fixed by a lathe chuck and spun at high speeds, cutting tools are used to carve complex and detailed shapes. Such automation minimizes the chances of mistakes and boosts overall productivity in the machining sequence.
Key Components of a CNC Lathe: Spindle, Cutting Tool, and More
Every CNC Lathe contains a Spindle at its center, which spins the workpiece at high rotational energy. A mounted tool on the tool post is adeptly set to dismantle portions of the workpiece. Moreover, an additional vital component is the headstock, which contains the spindle and the tailstock, which serves the purpose of supporting the end portion of the workpiece, especially when it is long and heavy. Knowing these components of the machine will assist in making the CNC lathe perform to the machine’s peak parameters.
How Does a CNC Lathe Rotate and Shape a Workpiece?
The CNC lathe rotates the workpiece such that the cutting tool can accurately remove the required amount of material. The spindle rotation brings the cutting tool to a predetermined position, which results in the removal of material in the form of grooves, shafts, and other parts with high precision. This is called CNC turning. With CNC turning, it is much easier for machinists to create parts with complex geometries which otherwise would be extremely hard to achieve manually.
How Does a CNC Mill Differ from a CNC Lathe?
The Difference Between a CNC Lathe and a CNC Mill
Although both CNC lathes and CNC mills perform precision machining, their modes of operation differ. A CNC lathe will spin the workpiece hands-free against a fixed cutting tool. In contrast, a CNC mill will move its cutting tool hands-free against a stationary workpiece. This fundamental difference allows more complex shapes to be made on CNC mills, thereby catering to a wider variety of materials and geometric complexities.
When to Use a CNC Lathe or CNC Mill in Your Projects
Choosing between a CNC lathe and a CNC mill depends on the specific requirements of your project. If your work involves creating cylindrical parts or requires high rotational speeds, a CNC lathe is the preferred choice. Conversely, if your project demands intricate milling of flat or irregular surfaces, a CNC mill is more suitable. Understanding these distinctions will help you select the right machine for your needs.
Exploring the Precision and Versatility of CNC Milling Machines
CNC milling machines are famous for their precision and versatility. They can do many operations such as drilling, cutting, contouring, and engraving. Their versatility allows the use of different types of cutting tools, like end mills, which are made from metal, alloys, and wood. Because of their flexibility and multiple uses, these machines are extremely helpful in any machine shop.
What Are the Benefits of Using a CNC Lathe and CNC Mill?
Precision Machining: Achieving High Tolerance Levels
Achieving high tolerance levels is one of the primary advantages offered by CNC machines. The process of precision machining guarantees every manufactured part is exact, minimizing discrepancies and enhancing quality. Maintaining this high level of accuracy is critical in industries that cannot withstand even the slightest variation.
Enhancing Efficiency in Metalworking and Woodworking
CNC lathes and mills are important modern tools that increase productivity tremendously in metalworking and woodworking. The automated features of these machines enable faster production and less handling, which results in lower labor costs and high output. Such efficiency is critical within any fast-moving business environment.
Why Machinists Prefer CNC Machines for Complex Projects
CNC machines have become an essential tool for most machinists due to the complexity of CAD projects and their ability to work on elaborate designs and difficult materials. Their precision and repeatability make CNC machines the best suited for parts that must be produced within a certain tolerance level. Moreover, the sophisticated control programs that are offered today make effortless changes and fine adjustments possible, thus ensuring that every project is done to perfection.
What Are the Common Applications of CNC Lathes and Mills?
Exploring the Use of CNC Machines in Metalworking Industries
CNC machining centers are popular in the metalworking industry for the processes of cutting, drilling, and shaping a metal component. They can work with steel, aluminum, and various alloys, which enables the production of high-quality parts with great precision, speed, and ease.
The Role of CNC Lathes in Wood Turning and Woodworking
CNC lathes are crucial for wood turning and woodworking since they enable users to make elaborate designs easily. The accuracy of CNC machinery guarantees perfection on all pieces, be it a decorative part or a simple spindle.
Innovative Applications: From Mini Lathes to Large-Scale Projects
CNC machines can be used for an array of applications, ranging from small-scale hobby projects such as benchtop lathes to large-scale industrial CNC machines used for mass production. With this degree of flexibility, wide-ranging industries are served, and cross-application challenges are met.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between a CNC lathe and a CNC mill?
A: A CNC lathe and a CNC mill differ primarily in their purpose. A CNC lathe will machine cylindrical parts as the workpiece rotates on a spindle, while the cutting tool stays still. On the other hand, a CNC mill does not rotate the workpiece, which remains still, but uses propeller-shaped tools as cutters, thus able to create flat surfaces along with complicated shapes.
Q: What are the advantages of using a lathe mill combo machine?
A: Once you have a lathe mill combo, both turning and milling operations can be performed with the same machine, giving them the advantage of flexibility and multi-functionality. Furthermore, machining activities such as cutting and even milling can be performed using just one machine; therefore, these units are space and cost-efficient with great versatility.
Q: Can a wood lathe be used for metalworking?
A: No, a wood lathe cannot be utilized for metalworking purposes. It does not possess the required features to perform such operations. For example, metal lathes need more rugged parts, a higher spindle speed, and a much sturdier construction than a wood lathe offers to achieve tight tolerances while machining tougher metals.
Q: In what ways does a CNC mill customize every machine differently?
A: Each CNC mill has a distinct designed skill set, like spindle speed, axis configuration, and types of cutting tools, which dictate what machining processes will be used. Because of these differences, CNC mills can service aerospace as well as automotive industries, providing customized machining services.
Q: What are the advantages of using a desktop CNC milling machine?
A: With a specific focus on small-scale projects, desktop CNC devices are more affordable and easier to acquire than their larger counterparts. The CNC desktop milling machines are aimed at educators, small businesses, and even hobbyists, enabling the production of precise parts and components without huge industrial equipment.
Q: Which materials are suitable for machining with a CNC lathe and a CNC mill?
A: A CNC lathe and mill can machine most materials, including different metals such as steel and aluminum, plastics, and even some composites. The material selection is based on the application and the characteristics required for the final product, like strength, weight, and resistance to corrosion.
 Cnc Milling Machine Parts High Precision Cnc Machine Parts List PdfNegotiableMOQ: 1 PieceBrand Name: JunzhuPlace of Origin: ChinaShijiazhuang Junzhu Technology Co., Ltd1 Yr
Cnc Milling Machine Parts High Precision Cnc Machine Parts List PdfNegotiableMOQ: 1 PieceBrand Name: JunzhuPlace of Origin: ChinaShijiazhuang Junzhu Technology Co., Ltd1 Yr CNC Machining, Mechanical Parts, Lathe Processing Services, Milling PartsNegotiableMOQ: 1 PieceTransport Package: Carton boxTrademark: TSOrigin: ChinaGusu District Qiusheng Commercial Equipment Firm1 Yr
CNC Machining, Mechanical Parts, Lathe Processing Services, Milling PartsNegotiableMOQ: 1 PieceTransport Package: Carton boxTrademark: TSOrigin: ChinaGusu District Qiusheng Commercial Equipment Firm1 Yr CNC Router CNC Milling Machine CNC Carving MachineUS$ 1300 - 8000MOQ: 1 ComboDaoran Trade (Jilin) Co., Ltd,2 Yrs
CNC Router CNC Milling Machine CNC Carving MachineUS$ 1300 - 8000MOQ: 1 ComboDaoran Trade (Jilin) Co., Ltd,2 Yrs Nylon Pa6 Plastic Machining and Lathe Milling Parts for Textile and Farm MachineryUS$ 2 - 8MOQ: 1 PieceBrand Name: 889776Place of Origin: ChinaModel Number: 2002966Dezhou Mande Import & Export Co.,Ltd.1 Yr
Nylon Pa6 Plastic Machining and Lathe Milling Parts for Textile and Farm MachineryUS$ 2 - 8MOQ: 1 PieceBrand Name: 889776Place of Origin: ChinaModel Number: 2002966Dezhou Mande Import & Export Co.,Ltd.1 Yr Factory Precision CNC Machining Milling Alloy Steel Wear Resistant Lining PlateNegotiableMOQ: 1 Square MeterBrand Name: WODONType: Steel PlateApplication: Ship PlateSurface Treatment: CoatedJiangsu Wodon Wear Resistant New Material Co., Ltd.1 Yr
Factory Precision CNC Machining Milling Alloy Steel Wear Resistant Lining PlateNegotiableMOQ: 1 Square MeterBrand Name: WODONType: Steel PlateApplication: Ship PlateSurface Treatment: CoatedJiangsu Wodon Wear Resistant New Material Co., Ltd.1 Yr CNC Milling Lathe Machine XH7132US$ 15,000 - 18,000MOQ: 1 UnitBrand Name: HAISHUPlace of Origin: Shandong, ChinaCondition: NewHorizontal Lathe Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
CNC Milling Lathe Machine XH7132US$ 15,000 - 18,000MOQ: 1 UnitBrand Name: HAISHUPlace of Origin: Shandong, ChinaCondition: NewHorizontal Lathe Co., Ltd.5 Yrs Mini Cnc Lathe Milling MachineUS$ 9,000 - 10,000MOQ: 1 SetCondition: NewCNC or Not: CNCPlace of Origin: ChinaBrand Name: fastcutJinan Zhongtang Mechanical Equipment Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
Mini Cnc Lathe Milling MachineUS$ 9,000 - 10,000MOQ: 1 SetCondition: NewCNC or Not: CNCPlace of Origin: ChinaBrand Name: fastcutJinan Zhongtang Mechanical Equipment Co., Ltd.5 Yrs CNC Lathe, Cnc Machining, Milling Spare Parts for Electric MotorUS$ 0.1 - 10MOQ: 10 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Milling, Other Machining Services, Rapid PrototypingMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningShanghai Yunkai International Trading Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
CNC Lathe, Cnc Machining, Milling Spare Parts for Electric MotorUS$ 0.1 - 10MOQ: 10 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Milling, Other Machining Services, Rapid PrototypingMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningShanghai Yunkai International Trading Co., Ltd.5 Yrs China Professional CNC Machining Machinery Parts Cnc Lathe and Milling PartsUS$ 0.01 - 3.58MOQ: 50 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Laser Machining, Milling, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningShenzhen Yaopeng Metal Products Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
China Professional CNC Machining Machinery Parts Cnc Lathe and Milling PartsUS$ 0.01 - 3.58MOQ: 50 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Laser Machining, Milling, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningShenzhen Yaopeng Metal Products Co., Ltd.5 Yrs High Precision Cnc Machined Aluminium Parts/cnc Lathe Turning Parts/cnc Lathe Milling PartsUS$ 1 - 100MOQ: 1 PieceCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Etching / Chemical Machining, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, Wire EDMMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningDalian Hongsheng Machine Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
High Precision Cnc Machined Aluminium Parts/cnc Lathe Turning Parts/cnc Lathe Milling PartsUS$ 1 - 100MOQ: 1 PieceCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Etching / Chemical Machining, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, Wire EDMMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningDalian Hongsheng Machine Co., Ltd.5 Yrs HEFEI SUDA Milling Machine MACHINES FOR PVC CNC WOOD LATHE SD8070NegotiableMOQ: 1 PieceCondition: NewCNC or Not: CNCPlace of Origin: Anhui, ChinaBrand Name: SUDATongxing Technology Development Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
HEFEI SUDA Milling Machine MACHINES FOR PVC CNC WOOD LATHE SD8070NegotiableMOQ: 1 PieceCondition: NewCNC or Not: CNCPlace of Origin: Anhui, ChinaBrand Name: SUDATongxing Technology Development Co., Ltd.5 Yrs Stainless Steel Small Milling Machine Lathe Parts Cnc MachiningUS$ 0.5 - 10MOQ: 500 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, Rapid Prototyping, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Not Micro MachiningQingdao Tianluli Industrial Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
Stainless Steel Small Milling Machine Lathe Parts Cnc MachiningUS$ 0.5 - 10MOQ: 500 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, Rapid Prototyping, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Not Micro MachiningQingdao Tianluli Industrial Co., Ltd.5 Yrs Wuhan Mill Provide Automatic Wood CNC Machine Wood Lathe MachineUS$ 5,000 - 8,000MOQ: 1 SetCondition: NewCNC or Not: CNCPlace of Origin: Hubei, ChinaBrand Name: JOYWuhan King Suntime CNC Equipment Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
Wuhan Mill Provide Automatic Wood CNC Machine Wood Lathe MachineUS$ 5,000 - 8,000MOQ: 1 SetCondition: NewCNC or Not: CNCPlace of Origin: Hubei, ChinaBrand Name: JOYWuhan King Suntime CNC Equipment Co., Ltd.5 Yrs Cnc Lathe Machine/wood Cnc Milling Machine/cnc Machine Price in IndiaUS$ 36,000 - 40,000MOQ: 1 SetBrand Name: MMCNCModel Number: SKX3+1-CNC-3000Sinon CNC Machine Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
Cnc Lathe Machine/wood Cnc Milling Machine/cnc Machine Price in IndiaUS$ 36,000 - 40,000MOQ: 1 SetBrand Name: MMCNCModel Number: SKX3+1-CNC-3000Sinon CNC Machine Co., Ltd.5 Yrs Precision CNC Milling and Lathing ComponentsUS$ 1 - 20MOQ: 200 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Etching / Chemical Machining, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, Turning, Wire EDM, Rapid PrototypingMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel Alloys, Aluminum, Brass, Other, Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel Alloys, Aluminum, Brass, StainleMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningNingbo Beilun Yinghui Industrial Parts Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
Precision CNC Milling and Lathing ComponentsUS$ 1 - 20MOQ: 200 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Etching / Chemical Machining, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, Turning, Wire EDM, Rapid PrototypingMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel Alloys, Aluminum, Brass, Other, Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel Alloys, Aluminum, Brass, StainleMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningNingbo Beilun Yinghui Industrial Parts Co., Ltd.5 Yrs Precision CNC Lathe and Milled PartsUS$ 0.01 - 11MOQ: 100 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Etching / Chemical Machining, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningDongguan INT Metal Products Factory5 Yrs
Precision CNC Lathe and Milled PartsUS$ 0.01 - 11MOQ: 100 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Etching / Chemical Machining, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningDongguan INT Metal Products Factory5 Yrs CNC Lathe Part, Lathe MachiningUS$ 0.01 - 1MOQ: 100 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Etching / Chemical Machining, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, Turning, Wire EDM, Rapid PrototypingMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningRun Sheng Plastic Hardware Co., Ltd.4 Yrs
CNC Lathe Part, Lathe MachiningUS$ 0.01 - 1MOQ: 100 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Etching / Chemical Machining, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, Turning, Wire EDM, Rapid PrototypingMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningRun Sheng Plastic Hardware Co., Ltd.4 Yrs High Precision Cnc Lathe and Cnc Milling PartsNegotiableMOQ: 1 PieceCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Etching / Chemical Machining, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, Turning, Wire EDM, Rapid PrototypingMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningShenzhen Keyuanhua Plastic And Metal Product Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
High Precision Cnc Lathe and Cnc Milling PartsNegotiableMOQ: 1 PieceCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Etching / Chemical Machining, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, Turning, Wire EDM, Rapid PrototypingMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningShenzhen Keyuanhua Plastic And Metal Product Co., Ltd.5 Yrs CNC Lathe Machined PartsUS$ 0.15 - 10MOQ: 100 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless Steel, Other, Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless Steel, metalMicro Machining or Not: Not Micro MachiningDongguan Weimi Hardware Products Factory5 Yrs
CNC Lathe Machined PartsUS$ 0.15 - 10MOQ: 100 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless Steel, Other, Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless Steel, metalMicro Machining or Not: Not Micro MachiningDongguan Weimi Hardware Products Factory5 Yrs CNC Lathe MachineUS$ 8 - 10MOQ: 1 PieceCondition: NewType: Turning CenterCNC or Not: CNCAutomatic Grade: AutomaticGran Brothers Company Ltd.5 Yrs
CNC Lathe MachineUS$ 8 - 10MOQ: 1 PieceCondition: NewType: Turning CenterCNC or Not: CNCAutomatic Grade: AutomaticGran Brothers Company Ltd.5 Yrs Cnc Lathe Machine PartNegotiableMOQ: 1 PiecePlace of Origin: Shanghai, ChinaBrand Name: OEMType: Machining PartsMaterial: Other, Alloy, Aluminium AlloyShanghai Ninefold Import Export Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
Cnc Lathe Machine PartNegotiableMOQ: 1 PiecePlace of Origin: Shanghai, ChinaBrand Name: OEMType: Machining PartsMaterial: Other, Alloy, Aluminium AlloyShanghai Ninefold Import Export Co., Ltd.5 Yrs CK6032 CNC Lathe MachineNegotiableMOQ: 1 SetCondition: NewType: HorizontalCNC or Not: CNCAutomatic Grade: AutomaticL&T Mechanical & Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
CK6032 CNC Lathe MachineNegotiableMOQ: 1 SetCondition: NewType: HorizontalCNC or Not: CNCAutomatic Grade: AutomaticL&T Mechanical & Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd.5 Yrs CNC Lathe Machine PartsUS$ 0.01 - 100MOQ: 100 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless SteelPlace of Origin: Shandong, ChinaModel Number: OEMQingdao Regenco Industry Co., Limited5 Yrs
CNC Lathe Machine PartsUS$ 0.01 - 100MOQ: 100 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless SteelPlace of Origin: Shandong, ChinaModel Number: OEMQingdao Regenco Industry Co., Limited5 Yrs CNC Machining LatheNegotiableMOQ: 1000 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Drilling, Milling, Other Machining Services, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysPlace of Origin: Guangdong, ChinaSUNYON Industry Co., Ltd. Dongguan China5 Yrs
CNC Machining LatheNegotiableMOQ: 1000 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Drilling, Milling, Other Machining Services, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysPlace of Origin: Guangdong, ChinaSUNYON Industry Co., Ltd. Dongguan China5 Yrs Cnc Lathe Machine ShaftUS$ 0.15 - 0.2MOQ: 5000 PiecesPlace of Origin: Guangdong, ChinaBrand Name: JIACAI, JIACAIModel Number: JC-0011Type: Other, Furniture BoltDongguan Jiacai Hardware Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
Cnc Lathe Machine ShaftUS$ 0.15 - 0.2MOQ: 5000 PiecesPlace of Origin: Guangdong, ChinaBrand Name: JIACAI, JIACAIModel Number: JC-0011Type: Other, Furniture BoltDongguan Jiacai Hardware Co., Ltd.5 Yrs Purchasing Director requested a quote for cnc metal prototype spinning lathe parts metal spun milling parts2025-10-26 17:15:22
Purchasing Director requested a quote for cnc metal prototype spinning lathe parts metal spun milling parts2025-10-26 17:15:22 Purchaser placed an order for custom precision cnc lathe machining parts2025-10-28 06:07:15
Purchaser placed an order for custom precision cnc lathe machining parts2025-10-28 06:07:15 Procurement Specialist negotiating terms for High Precision CNC Machining Parts - Lathe Machining2025-10-29 19:54:01
Procurement Specialist negotiating terms for High Precision CNC Machining Parts - Lathe Machining2025-10-29 19:54:01 Importer is sourcing OEM CNC machined part cnc milling cnc machining part2025-10-29 06:14:21
Importer is sourcing OEM CNC machined part cnc milling cnc machining part2025-10-29 06:14:21 Verified Buyer verified certifications for lcd dsp controller for cnc lathe/dsp controller for engrving machine2025-10-27 07:05:21
Verified Buyer verified certifications for lcd dsp controller for cnc lathe/dsp controller for engrving machine2025-10-27 07:05:21 Procurement Lead submitted an RFQ for Factory Price CNC Cutting Milling Machine15 hours ago
Procurement Lead submitted an RFQ for Factory Price CNC Cutting Milling Machine15 hours ago Procurement Lead verified certifications for stainless steel cnc engraving milling machine2025-10-25 15:32:39
Procurement Lead verified certifications for stainless steel cnc engraving milling machine2025-10-25 15:32:39 CNC Lathe Processing/ CNC Turning/CNC Milling Aluminum ProductUS$ 5 - 10MOQ: 500 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Etching / Chemical Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningKunshan Prosperity Metal Products Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
CNC Lathe Processing/ CNC Turning/CNC Milling Aluminum ProductUS$ 5 - 10MOQ: 500 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Etching / Chemical Machining, Milling, Other Machining Services, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningKunshan Prosperity Metal Products Co., Ltd.5 Yrs Hot Sale Mini 5 Axis Cnc Routers Milling Lathe Machine Remaix 1224US$ 135,000 - 185,000MOQ: 1 SetCondition: NewCNC or Not: CNCPlace of Origin: Shandong, ChinaBrand Name: RemaxJinan Remax Machinery Technology Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
Hot Sale Mini 5 Axis Cnc Routers Milling Lathe Machine Remaix 1224US$ 135,000 - 185,000MOQ: 1 SetCondition: NewCNC or Not: CNCPlace of Origin: Shandong, ChinaBrand Name: RemaxJinan Remax Machinery Technology Co., Ltd.5 Yrs OEM Lathe Mill Machine PartUS$ 0.1 - 100MOQ: 50 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Laser Machining, Milling, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningShenzhen Hafond Technology Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
OEM Lathe Mill Machine PartUS$ 0.1 - 100MOQ: 50 PiecesCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Laser Machining, Milling, TurningMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Hardened Metals, Precious Metals, Stainless Steel, Steel AlloysMicro Machining or Not: Micro MachiningShenzhen Hafond Technology Co., Ltd.5 Yrs China Cnc Lathe Machine Htc80US$ 1,000 - 10,000MOQ: 1 SetPlace of Origin: Jiangsu, ChinaBrand Name: TONG WEIModel Number: QC11Y/KHigh Quality Cheap Prices steel sheet cutting machineNantong Weili CNC Machine Tool Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
China Cnc Lathe Machine Htc80US$ 1,000 - 10,000MOQ: 1 SetPlace of Origin: Jiangsu, ChinaBrand Name: TONG WEIModel Number: QC11Y/KHigh Quality Cheap Prices steel sheet cutting machineNantong Weili CNC Machine Tool Co., Ltd.5 Yrs Precision Aluminium Cnc Lathe MachiningUS$ 2.59 - 3.09MOQ: 1 TonCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining ServicesMaterial Capabilities: AluminumMicro Machining or Not: Not Micro MachiningShanghai Jiayun Aluminium Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
Precision Aluminium Cnc Lathe MachiningUS$ 2.59 - 3.09MOQ: 1 TonCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Laser Machining, Milling, Other Machining ServicesMaterial Capabilities: AluminumMicro Machining or Not: Not Micro MachiningShanghai Jiayun Aluminium Co., Ltd.5 Yrs CNC Milling Machine PartsUS$ 1 - 10,000MOQ: 1 TonPlace of Origin: Shanxi, ChinaBrand Name: SYIApplication: Industrial useMaterial: SteelSYI Industrial Co., Ltd.5 Yrs
CNC Milling Machine PartsUS$ 1 - 10,000MOQ: 1 TonPlace of Origin: Shanxi, ChinaBrand Name: SYIApplication: Industrial useMaterial: SteelSYI Industrial Co., Ltd.5 Yrs Cnc Machine Milling ManufacturingUS$ 50 - 200MOQ: 1 SetCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Milling, Turning, Rapid PrototypingMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Stainless Steel, Other, Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Stainless Steel, plasticMicro Machining or Not: Not Micro MachiningShenzhen Ebyton Technology Ltd.5 Yrs
Cnc Machine Milling ManufacturingUS$ 50 - 200MOQ: 1 SetCNC Machining or Not: CNC MachiningType: Broaching, Drilling, Milling, Turning, Rapid PrototypingMaterial Capabilities: Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Stainless Steel, Other, Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Stainless Steel, plasticMicro Machining or Not: Not Micro MachiningShenzhen Ebyton Technology Ltd.5 Yrs














