From ensuring safe drinking water to purifying the air in factories, filtration has become essential to various industries. But what if we told you that meeting the operational requirements for your complex processes does not need to be a hassle? This article uncovers the tools and technologies that optimize performance and drive efficiency stemming from the science and tactics behind ‘filter equipment.’ Whether your goal is to enhance operational sustainability, increase productivity levels, or advance needs for regulations, this article is filled with insights tailored toward making confident and informed decisions. Unlock the true potential that modern filter equipment offers as we delve into its possibilities.
What is Filter Equipment, and How Does It Work?
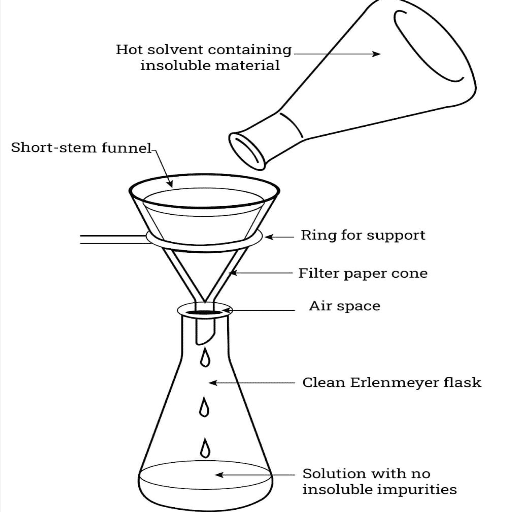
Air filter equipment removes unwanted particles, impurities, or contaminants, such as dust, from gases, liquids, and other substances. This is done through barriers such as mesh, membranes, and filter media, which trap these unwanted elements while allowing the target material to pass through. The purpose of filters depends highly on the application, such as air improvement, industrial processes, or water purification. Filter equipment increases operational efficiency through cleaner outputs while ensuring machinery reliability and safety in varying environments.
Understanding the Basics of Filtration Systems
Different filtration systems serve distinct functions and specific environments. The main categories are mechanical, chemical, and biological filtration. Mechanical filtration uses physical barriers such as meshes or membrane filters to extract suspended solids from fluids. This method is extensively used in water purification and industrial systems where some advanced filters can extract particles as small as 0.01 μm. For example, HEPA filters used in air purification can capture 99.97% of particles down to 0.3 μm, improving air quality.
Chemical filtration employs activated carbon and ion exchange resins to ionically separate contaminants. Carbon filtration is efficient in neutralizing odor, chlorine, and organic chemicals. Biological filtration, standard in aquariums or wastewater treatment plants, uses beneficial microorganisms to compounds such as ammonia or nitrate.
Recent advancements in filtration technologies focus on energy efficiency, longer filter lifespans, and the application of nanotechnology to improve filtration efficiency. One unmet filtration need is high-permeability membranes capable of trapping ultrafine particles. Nanofibrous membranes are proving to be a popular choice for these applications. These technologies help solve global problems like water scarcity and air pollution by providing cleaner resources to various industries.
Key Components of Filter Equipment
The filter equipment consists of some significant elements, each of which serves a unique purpose in ensuring effective filtration in different application areas. Provided below is a brief description of the essential components and their functions:
Filter Media: The essential component of any filtration system is its filter media, which aims to capture and retain particles. Some different filter media types are woven fabrics, mesh materials, activated carbon, or advanced nanofibrous membranes. A good example is HEPA filters, which are used in air filtration. These filters can capture 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 microns in size.
Housing Units: These durable housings guard the filter media and ensure proper system functioning under challenging conditions. The protective materials are Stainless steel, polycarbonate, and polypropylene, which are selected depending on the application needs, such as chemical resistance, how much pressure they can withstand, or what temperatures they can endure.
Flow Control Mechanisms: Proper flow control handles the velocity at which fluids or air pass through the filter media. Regulators, valves, and bypass systems are commonly used to maintain a particular flow rate and avoid a pressure drop.
Support Structures: Grids or frames that form the filter media are sustainably arranged and do not allow for collapse or deformation from enormous pressure. These structures enhance the filter media’s efficiency by increasing its overall usable surface area.
Sealing Systems: Effective sealing stops contaminants from bypassing the system and ensures that unfiltered air or liquids do not seep out. The integrity of the seals is maintained, and these gaskets, O rings, adhesives, and other sealing materials must be of high quality.
Monitoring and Diagnostic Tools: Many new systems integrate pressure sensors and flow meters to monitor real-time performance. This enables faster identification of clogs or maintenance issues, improving system uptime. Some systems also have IoT devices that transmit real-time data for predictive maintenance.
Energy-Efficient Designs: Growing concerns regarding energy consumption are affecting filtration systems. Modern equipment often incorporates low-energy fans, pumps, and blowers to offset operational costs while still maintaining a high level of filtration.
Modern filtration systems, for example, can confront new challenges such as ultrafine particle filtration, hazardous waste filtration, and water purification at an unprecedented level by combining these components and technologies. Also, implementing nanotechnology into filters has dramatically reduced power consumption by 30% while meeting stringent clean air and water requirements. These advancements signal that increased innovation continues to drive filtration equipment design.
Common Applications of Filtration Solutions
Numerous industries utilize filtration solutions to keep business processes running smoothly and to resolve particular issues. One of the main applications is in water treatment facilities, where filters remove contaminants, improving water quality and compliance with safety regulations. Membrane filtration systems, for example, are found in municipal water treatment plants to remove bacteria, viruses, and other harmful particles, ensuring millions have access to clean drinking water.
The other important application is within the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries. Filtration systems must maintain sterile environments, specifically in hospitals, laboratories, and drug manufacturing. HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are used extensively, capturing 99.97% of airborne contaminants of 0.3 microns in size and considerably decreasing the chance of contamination.
Filtration solutions are also standard in the industrial sector, including oil and gas refining, chemical production, food processing, etc. Refineries, for example, use catalytic filtration systems to enhance the quality of end products by removing impurities from crude oil. Furthermore, food and beverage producers employ filtration technologies to extract undesirable particles from their products, guaranteeing consumer safety and quality.
Filtration technologies also serve as environmental protection tools. Air filtration systems are increasingly being installed to limit the escape of harmful particulates such as PM2.5 and VOCs from industrial plants into the environment. Recent research has shown that installing air filtration systems in factories and densely populated areas has decreased air pollution levels, thus improving the population’s health.
Air and oil filters are critically important for any vehicle in the automotive industry. They help maintain the engine’s efficiency, control the level of harmful substances being emitted, and ensure that the air entering the cabin is clean. With the increased emphasis on sustainability, eco-friendly materials for filter manufacture and more easily recyclable filters are rising.
Such examples showcase the importance of filtration technology and its impact on safety, efficiency, environmental protection, and sustenance in diverse fields.
How to Choose the Right Filter for Your Needs?

Finding the correct filter is determined by your personal needs. For instance, identify which application filters fit into: air, water, or fuel. Additionally, consider how deep the filter must be, from large particles needing removal to microscopic contaminants needing elimination. Check if the filter is compatible with your system to ensure proper function. Finally, prioritize quality and sturdiness by picking filters from reliable manufacturers to ensure enduring efficiency. Always follow the instructions and recommendations provided by the manufacturer’s guidelines to make the right choice for your needs.
Factors to Consider in Filter Design
An effective filtration system has several components that need to be assessed. Efficiency and reliability are two key aspects to consider.
Filtration Efficiency and Ratings: Efficiency metrics reservations, minimum efficiency reporting value or MERV rating, and HEPA (high-efficiency particulate air) standards also apply to filters. An example is HEPA filters, which are required to capture 99.97% of particles of 0.3 microns. Filters differ depending on whether they are for industrial or residential use, which makes choosing the proper efficiency rating vital.
Flow Rate and Pressure Drop: The relationship between optimal filtration and airflow must be maintained for the system to perform effectively. Systems strain and energy costs increase when using high-pressure drop filters. Studies indicate that selecting filters designed to keep a low-pressure drop while achieving high filtration can improve overall HVAC system performance by up to 20–30%. Considering the system’s operational requirements for the filter’s pressure drop performance is essential.
Media and Filter Materials: The filter media type, fiberglass, pleated paper, or activated carbon, impacts durability and performance. For example, activated carbon filters are particularly good at removing odor and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from the air. They are used in chemically sensitive indoor environments such as hospitals and chemical labs.
Environmental Factors: Filter performance must be tailored to the conditions in which the filters will be used. For example, areas with high humidity will need mold-resistant materials, while high-particulate industrial environments may require pre-filters to protect primary filters and extend their lifespan.
Filters Life Cycle And Replacement Cost: A filter’s lifecycle cost includes more than its purchase cost. Economically, filters that require less servicing in intervals are more cost-efficient. HVAC studies indicate that proactive maintenance, especially timely servicing of the filters, can reduce energy consumption by 15%.
Industry Compliance: Using all applicable standards, such as ASHRAE and ISO filter performance and safety benchmarks, increases the trust that the filters will deliver dependable results regardless of the application.
Considering these factors will allow the construction of a filtration system that achieves the optimal performance, durability, and cost-efficiency balance required for the specified application.
Evaluating Filter Performance Standards
While reviewing the filter standards, one must pay attention to the criteria set by specific groups regarding air quality and safety because they established metrics and benchmarks. An example of these notable standards is ASHRAE 52.2, which measures the particulate air filter efficiency using a system of ratings known as MERVs, and the ISO 16890 standard, which classifies air filters according to the particulate matter they can capture (PM1, PM2.5, PM10). These two standards allow for assessing a filter’s efficiency in removing contaminants from the air.
For example, a MERV rating of 13 to 16 indicates the level of filtration done is high enough to be used in places such as hospitals and other commercial buildings. Likewise, ISO 16890 provides an international standard that ensures filters are categorized and named based on actual working particulate levels and gives users a genuine sense of how well the filters work. Current studies emphasize the increasing importance of filters that capture ultrafine particles (PM1) due to their rising association with health concerns.
Working alongside performance criteria also guarantees consistency with specific HVAC systems. For filters, higher MERV or ePM1 ratings can be problematic in some systems as they tend to be too restrictive, leading to increased energy usage. Considering these multiple factors ensures that filters achieve the desired maintenance level while simultaneously fulfilling energy efficiency criteria, broadening the industry’s sustainability criteria.
Custom Solutions for Unique Filtration Requirements
Different industries and environments present unique challenges, especially regarding modern filtration demands, which require tailored solutions. In the healthcare sector, for example, specialized HEPA filters are necessary to ensure a sterile environment for patient safety by capturing 99.97 percent of particulate contaminants as small as 3 microns. Likewise, ULPA filters are used in the cleanroom manufacturing of pharmaceuticals or electronics for an even greater level of air purity.
Emerging innovations in filtration technology place traditional filtration materials alongside progressive features like activated carbon layers for odor and VOC discharge, antimicrobial coatings to inhibit bacterial growth, and more advanced nanotechnology focused on developing electrospun nanofibers that can capture ultrafine and even sub-0.1 micrometer pollutants.
Data highlights the importance of aligning operational practices and filtration solutions. For example, research shows an energy penalty when using incorrectly sized filters, and HVAC systems are estimated to consume up to 15 percent more energy in poorly optimized conditions. Performance and energy efficiency equilibria can be maintained using custom-engineered filters designed around specific airflow and pollutant capture needs.
Intelligent monitoring systems incorporating IoT-enabled sensors for real-time tracking of filter performance further enhance these tailored approaches. Such systems can offer predictive maintenance alerts, lowering operational downtime while increasing filter lifespan and yielding lower costs. Custom solutions additionally address evolving compliance and environmental concerns while improving the range of clean air operations.
What Are the Different Types of Filter Equipment?

Filter equipment is subdivided into different types depending on the filtration features required. The most common types are:
Bag Filters – These capture industrial process dust and other particulates.
Cartridge Filters capture finer particles and contaminants from liquids or gases.
HEPA Filters – High-efficiency particulate filters used in cleanrooms and HVAC systems to remove allergens and microscopic dirt.
Activated Carbon Filters – Used to remove adsorbed odor, chemicals, and vapor from air or water.
Sand Filters – These are used to treat water by removing suspended particles.
Cyclone Separators – Used to separate heavier particulates from air or gas streams with centrifugal force.
Separators, bag filters, and cartridge filters contain dust from the environment. Filter cartridges capture mold spores, therefore helping to improve environmental cleanliness.
Liquid Filters: Bag Filter, Plate, and More
Liquid filters are essential in eliminating impurities and maintaining process efficiency and liquid quality in different industries. Below are some of the most common liquid filters, along with their areas of application:
Bag filters are popular in chemical processing, food and beverage, and water treatment. They efficiently remove particulates from liquids. Like all bag filters, their construction includes a porous bag made from polypropylene or nylon, which can capture 1 to 200-micron particles. Their ability to conserve energy due to their high dirt-holding capacity makes them ideal for moderate contamination applications.
Plate and Frame Filters: These filters utilize plates and frames to compress filter media, separating solids from liquids. They are standard for dewatering or liquid clarifying processes in the pharmaceutical, chemical, and food industries. Operating under high pressure gives this filter an advantage when performing intricate filtration tasks or working on thick fluids.
Cartridge Filters: For applications requiring frequent changes, cartridge filters use replaceable filter elements encased within a vessel. They can be made from various materials, including pleated polypropylene or stainless steel, and can filter particles as small as 0.2 microns. Because of their efficiency, they are used extensively in water drinking filtration, ultrapure water manufacturing, and other industrial processes that require fine filtration.
Self-Cleaning Filters: Self-cleaning liquid filters are designed to function without interruption for long periods. These modern filters remove contaminants using automated scrapers and backflushing. They are commonly used in oil refining, wastewater disposal, and paper production, significantly increasing productivity by minimizing downtime and maintenance expenditures.
Liquid filtration is crucial to ensure the purity of equipment and products and uphold environmental policies. Modern technological advances continuously aspire to meet the needs of the rapidly evolving industrial world with more efficient and environmentally friendly solutions.
Air Filtration Products: From Oil Mist to Air Quality Improvement
Air filtration is essential in industrial and environmental settings because it contributes to workers’ safety and health and improves air quality. Air filtration in oil mist removal is critical since it is a by-product of several manufacturing processes, such as machining, metalworking, and lubrication. Superlative air filtration systems eliminate all oil mist levels and decrease the risk of fire, equipment damage, and even worker injury. A recent report states that high-efficiency oil mist filters can recover 99.97% of 0.3-micron particles captured, which gets us closer to the set standards of safety air regulations.
Air filtration technologies now focus on dust, VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) elimination, and other contaminants. Installation of HEPA (High-Efficiency Particle Air) filter units also contributes to the strict Air Quality Standards while improving the energy efficiency of industrial HVAC systems. Modern air cleaning devices cut energy costs by 20% through effortless flow increases and lower resistance, leading to less operational expenses and harmful carbon emissions.
The advancement of air quality filtration systems integrates innovative technology with sensors. Such innovative technology uses sensors and the Internet of Things (IoT) to measure air quality in real time and adjust the filtration levels accordingly. Industries are adopting such technologies to keep pace with eco-friendly regulations and improve workplace comfort. This enables companies to enhance their sustainable development goals (SDGs) while increasing workplace productivity.
Specialized Filters: Candle Filters, Separators, and Beyond
CANDLE FILTERS: Solid-liquid separation processes have an extremely high filtration efficiency using a specialized filtration system known as candle filters. Candle filters can be used in harsher environments like chemical and pharmaceutical manufacturing plants owing to their precise particle retention capability. The candle filters utilize cylindrical filter elements known as ‘candles’ in which the constructs can operate at a high flow rate with stable filtration performance because they work under pressure. The ability of candle filters to reduce waste during chemical production separations is remarkable. These filters provide a greater than 99% separation efficiency.
SEPARATORS: Oil and oil product mixtures and gas and gas mixtures demand a specific gadget characterized by fluids and gases known as a separator. Separators segregate different substances based on density, item, and particle size. Effective separators can be tracked in wastewater treatment plants, where they help solve the environmental suspension solid and oil discharge problem. New research indicates these gas processing separator systems recover about 98% of hydrocarbons during oil and gas processing, reducing environmental impact and resource loss during extraction.
Creative Thinking Over Tradition: Modern filtration systems use more advanced materials, such as ceramic membranes and nanofibers, beyond ordinary systems. For example, nanofiber filters capture microscopic particles with a greater efficiency of more than 99.97% for particles greater than 0.3 microns. Likewise, ceramic membranes are increasingly used in high-temperature and corrosive settings because of their exceptional endurance and chemical resistance. These specialized materials are aiding the aerospace and semiconductor manufacturing sectors to cope with strict operational requirements and minimize downtime, demonstrating the continued advancement in specialized filtration technology.
What Role Does Filter Equipment Play in Industrial Applications?

In industrial applications, filter equipment helps maintain compliance with environmental laws, protects shareholders, and preserves the purity of essential materials. It removes contaminants from the air, liquids, or gases, thus enhancing the quality of the product and increasing equipment durability. Industries depend on the filtration system from manufacturing to energy production to maintain productivity, lower maintenance costs, and protect reliability.
Filtration Systems in the Chemical Industry
Within the chemical sector, filtration systems are critical as they guarantee the proper and effective handling of raw materials and the processing of finished products. These systems are also helpful with other functions like the recovery of catalysts, purification of solvents, removal of particulates, etc. For example, membrane separation is incredibly popular because it can produce good separation with low energy. These pieces of equipment are crucial in removing unwanted solids that could contaminate liquids, gases, and other process streams.
Advances in filtration have significantly impacted the chemical industry as a whole. Many analysts believe that the chemical sector globally faces a rising demand curve for membrane filtration molds above eight percent annually due to the factors above. Other innovations, like nanofiltration, have bolstered the capability to remove impurities at the molecular scale, allowing operations to run with minimum interruptions.
Filtration systems further allow businesses to meet their environmental obligations by preventing hazardous pollutants and wastes from being released into the environment for proper disposal. Stricter rules for controlling emissions are a basic necessity in some parts of the world, which makes it compulsory for other industries to adopt modern filtration techniques. Such equipment can meet these standards and greatly aids the recovery of some resources like precious metals or valuable solvents.
Modern filtration systems in the chemical industry have financial and ecological significance, marking their importance in contemporary chemical manufacturing processes.
Oil and Gas: Filtration Solutions for Natural Gas and Fuel
Oil and gas companies use advanced filtration technologies that guarantee that natural gas and fuels are pure and that production, processing, and distribution are efficient. There are greater-level filtration systems that help eliminate impurities like particulates, water, and hydrocarbons, which threaten to halt equipment operations or degrade the quality of the end product. Take natural gas pipelines: high-efficiency coalescing filters are instrumental in removing liquids and aerosols from gas streams, ensuring safety and reliability.
As the world modernizes, the supply and demand for clean energy alternatives rise, bringing greater focus to filtration systems. For example, the LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) production process requires extensive filtration to reduce fouling to a minimum and extract damaging impurities like sulfur compounds, which can corrode cryogenic processing equipment. Not to mention, sophisticated particulate filters embedded in modern engines are capable of ultra-fine filtration of 1 micron, optional for further reduction in emissions, enhanced engine performance, and dependable efficiency, which achieve these, too.
The latest information from the sector reveals the growth opportunities in oil and gas filtration solutions markets. The market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% from 2023 to 2030. This development is furthered by new policy regulations, heightened energy requirements, and the need for superior accuracy during refining processes requiring extreme filtration. The oil and gas industry relies heavily on filtration systems to enhance operational efficiency, cut costs, and meet environmental regulations. These systems are vital to maintaining a sustainable oil and gas industry.
Environmental Impact and Air Filtration Solutions
In response to increasing concerns about air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, air filtration technologies are being adopted due to the adverse effects of the oil and gas industry on the environment. Advanced filtration methods are now being used to capture other harmful emissions such as particulate matter (PM), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and sulfur oxides (SOx). A good example is HEPA filters and activated carbon systems, which have helped to lower airborne pollutants in industry.
Also, recent market research indicates that in the oil and gas industry, the global air filtration market will grow to 9.5 billion dollars by 2030 due to the adoption of emission control technology and compliance with environmental regulations like the Clean Air Act set forth by EPA. Major petroleum refineries are adopting newer technology, such as baghouse filters and electrostatic precipitators, to support cleaner production processes.
In addition, air filtration systems optimize performance, reducing operational downtime and prolonging machinery life. This advancement in equipment paired with eco-friendly solutions illustrates the relevance of air filtration systems as the industry adopts more responsible energy policies and environmentally sustainable practices.
How Does Filter Equipment Enhance Efficiency in Manufacturing?

Filter equipment increases manufacturing efficiency by allowing machinery to function at peak performance and keeping production processes free from contamination. These systems also assist in reducing equipment aging due to maintenance needs and unscheduled downtime by removing impurities from air, liquids, or gasses. Filtration further improves product value by reducing defects caused by impurities, which diminishes reworks and waste. As a result, operational efficiency is increased by smoother workflow, reduced operational expenses, consistent outputs, and enhanced accuracy.
Improving Air Quality in Industrial Facilities
Industrial facilities’ top priorities should be ventilation features and advanced filtration to improve air quality. At this moment, I would personally ensure periodic maintenance of the systems in place and procure HEPA filters to capture minute particles effectively. Modern sensors can track air quality and adjust automatically to solve problem areas that would otherwise exacerbate the problem. These measures make enhancing the working environment more healthily and safely possible.
Streamlining Processes with Efficient Filtration Systems
Correct filtration systems enhance air quality and improve the work processes of different industries. With modern technology, HEPA and ULPA filters can eliminate up to 99.97% of contaminants larger than 0.3 microns in diameter, thus improving clean air. Specialized electrostatic precipitators and activated carbon filters can remove VOCs and unpleasant smells, significantly improving air quality.
Recent studies claim that adopting advanced filtration systems reduces sick work days by 40%. With the new devices, workers become more productive, and there is less operational standstill. Additionally, monitoring devices paired with filtration systems make real-time changes and proactive adjustments far more straightforward, saving up to 30% in costs over time by avoiding system failures. With these technologies, businesses can improve the workplace atmosphere, fulfill legal requirements, and provide governmental and environmental regulations.
Adopting and improving filtration technologies enables companies to cut operational costs, streamline business processes, and provide a healthier workplace for staff and visitors.
Reducing Particulate Matter for Cleaner Production
Reducing particulate matter (PM) emissions in industrial operations is necessary for maintaining a cleaner environment. Activities such as combustion, material handling, and chemical reactions typically generate particulates in dust, soot, and other fine particles. Electrostatic precipitators and baghouse filters have advanced filtration and emission control technologies that capture more than 99% of airborne particulates, significantly reducing pollution.
Implementing the technologies above improves the air quality and conforms to demanding environmental regulations like those presented by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and other international bodies. Studies suggest that industries can adopt control measures to prevent thousands of tons of PM from being emitted each year, thus decelerating the adverse consequences on human beings and the ecosystem. Moreover, evolving real-time monitoring systems enable businesses to measure particulate levels more precisely, allowing further proactive measures.
Reference Sources
The following is a summary of relevant research on filtration equipment3:
-
Evaluation and Comparison of Performance in the Disc Filter with Sand Filters of Filtration Equipment in Micro Irrigation Systems1:
- Key Findings: This study evaluated the performance of disc filters with and without sand tanks in micro-irrigation systems. It found that sand tanks significantly improved the filtration efficiency when water contamination exceeded 100 mg/L. Without sand tanks, disc filters clogged faster, reducing their effectiveness.
- Methodology: The research involved setting up a central control system with various configurations of sand tanks and disc filters. Parameters like blockage duration, pressure loss, and filtration efficiency were measured over multiple experiments.
- Published: 2016.
-
Design of Water Treatment Plant Using SCADA and Coconut Shell as Capping for Sand in Rapid Sand Filters2:
- Key Findings: This study introduced the use of coconut shells as a capping material in rapid sand filters, which enhanced filtration efficiency and reduced maintenance costs. SCADA technology was integrated for real-time monitoring and control.
- Methodology: The research included designing a water treatment plant, testing coconut shells as a capping material, and comparing its performance with traditional sand. Results showed improved impurity removal and reduced backwash frequency.
- Published: 2019.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is filter equipment, and why is it essential in various industries?
A: Filter equipment removes solid particles from liquids or gases. It is crucial in power generation, pulp and paper, and paint manufacturing to ensure product quality and equipment longevity. Proper engineering and adhering to industry code standards are essential for optimal performance.
Q: How does pressure leaf filter equipment work?
A: Pressure leaf filters operate using multiple vertical or horizontal filter leaves enclosed in a tank. The liquid flows through the leaves, and solid particles are trapped, allowing the filtered liquid to transfer. This equipment is ideal for processes requiring high solids removal efficiency.
Q: What role does vacuum play in filter equipment operation?
A: Vacuum filter equipment, such as vacuum drum filters, uses a vacuum to draw liquid through a filter medium, leaving solids behind. This method is effective for filtering applications where delicate handling of materials is necessary, such as in the beer industry.
Q: How does filter equipment contribute to respiratory safety?
A: In environments with airborne solid particles, filter equipment is essential for purifying air, thus protecting workers’ respiratory health. Industrial filters capture dust, fumes, and other particulates, ensuring a safer working environment.
Q: Can filter equipment be customized to specific industry specifications?
A: Yes, filter equipment can be tailored to meet specific industry requirements and engineering standards, including size, material, and operation phase. This customization ensures that the equipment performs efficiently within its intended application.
Q: What are the benefits of using horizontal filter equipment?
A: Horizontal filter equipment offers advantages such as easier maintenance, space efficiency, and better handling of large volumes of material. This design is commonly used in applications like pulp processing, where horizontal configurations facilitate continuous operation.
Q: How is filter equipment used in the paint industry?
A: In the paint industry, filter equipment removes impurities and ensures a smooth, consistent product. Filters help achieve the desired paint specifications by removing clumps, particles, and contaminants during manufacturing.
Q: What is the significance of the transfer process in filter equipment operations?
A: The transfer process in filter equipment operations involves moving filtered liquids or gases to the next production phase. Efficient transfer is crucial for maintaining process flow and ensuring that the end product meets quality standards.
Q: How do companies like Filter Equipment co Inc. ensure product quality?
A: Companies like Filter Equipment Co Inc. ensure product quality by adhering to engineering best practices, meeting industry codes, and continuously innovating their designs. They focus on reliability, efficiency, and durability to meet diverse industrial needs.







