A distribution board, also termed a panel board or a breaker box, is considered an indispensable part of the electrical system of any house, edifice, or complex. It is the place that
ensures electricity is consumed safely and efficiently. However, what are the essential components of the distribution board such an important piece of technology, and what is its role in the more extensive electrical network? We will examine all the essential features of the distribution board and its importance in residential properties and commercial ones. By the end of this article, you shall fully understand the importance of this device in the current day and age of swift modernization. If you are looking for more information about go here right away!
What is a Distribution Board, and What Is Its Importance?
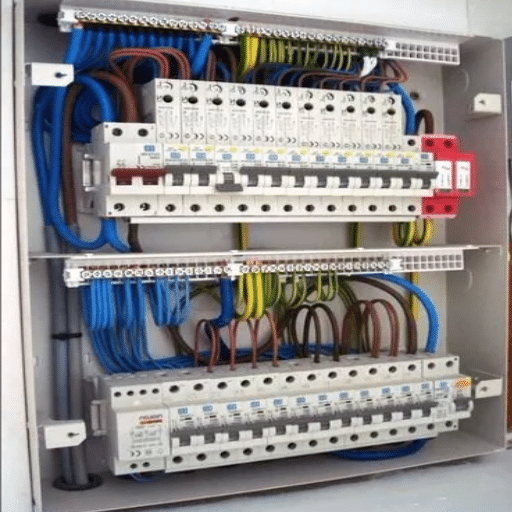
Definition of a Distribution Board
As a component of an electrical power system, a distribution board (also known as a panel board, breaker panel or electrical panel) is a unit that distributes an electrical supply to different circuits in a building or facility. It comprises circuits with protective devices like fuses or circuit breakers that prevent appliances and wires from overheating, shorting out, or suffering overcurrent damage.
Surge protectors and residual current devices (RCDs) are modern features added to contemporary distribution boards. These devices also meet moderate and stern industrial rules and regulations for reliability and risk management, thus offering a higher degree of safety for a user or system. Power distribution for homes, offices, industrial plants, and various other structures is tailored using these boards built to endure different capacities. Their modular and adaptable nature allows for scalability, supporting the increasing energy demands of today’s technology-driven environments.
The Function of Power Distribution Board in Electrical Systems
Power distribution boards help achieve effective and reliable management of electrical power distribution. They serve as the central point of electricity distribution, where centralized electricity is received and assigned to separate circuits. This segmentation improves energy management and system safety because each circuit is adequately protected against overloads and short circuits by means of circuit breakers or fuses.
Power consumption monitoring and intelligent performance diagnosis of electrical systems now form the progressive feature of modern power distribution boards. The additional features also made predictive maintenance possible. Moreover, the controlling bodies stress the distribution boards need good-quality insulation and adequate safeguards to reduce the risk of fire accidents and electric shocks. This leap forward renders power distribution boards as essential components for residential and industrial use, satisfying higher requirements of more sophisticated electrical systems and therefore providing increased control and protection in electrical systems.
In what manner does a distribution board improve electric risk management?
The distribution board is crucial to protecting electrical equipment and systems and its users by controlling and managing the electricity supply using an efficient system. The best example is the usage of circuit breakers and Residual Current Devices (RCD) or Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI). These systems work by cutting off power in case of an overload, short circuit, or leak flow, which helps to mitigate electrical fire and electrocution risks. In addition, the enclosures in modern distribution boards have fire retardant materials and insulation, which help prevent dangerous external faults.
These more advanced designs are often provided with intelligent monitoring systems that track electrical performance. These systems enable monitoring and allow the detection of problems such as a voltage drop or a current surge, which helps in prompt mitigation through damage control. Most often, there is a mandatory requirement to place multi-purpose labeled circuit arrangements with lockable enclosures, which gives control but also enables some freedom to authorized personnel only. By merging protective features concepts with modern technologies, distribution boards remain one of the most vital components for electrical safety in homes, offices, and even industrial buildings.
Types of Distribution Boards Used in Electrical Systems

Comparison of Different Types Of Electrical Distribution Boards
There are some differences that both cater to certain needs and are used for a particular purpose when talking about distribution boards. For instance, in main distribution boards, which are primarily used in larger-scale industrial shops, the power load capacity is significant, and power is distributed to numerous sub-panels. These boards are important to avoid balance issues in power flow and overloads in high-demand systems.
Sub-distribution boards are smaller and are intended for specific zones or areas within the building. The area is common in residential and commercial settings, permitting local electrical control. Modern flush-mounted boards are preferred for their design aesthetic as they sit within the walls and are often seen in modern urban apartments and offices looking to achieve a minimalistic design.
Last but not least, surface-mounted distribution boards are standard in utilities and industrial services because they have always been the easiest to install and maintain. They usually offer some level of rugged external protection by having robust casing. A decision from these types mostly depends on factors like the extent of work, weather conditions of the region, and the level of intimacy desired. Each sub-division provides some level of customization and control, making it easier to optimize electricity distribution systems.
The Differences Between Main Distribution Board and Sub Distribution Board
To the best of my knowledge, the different distribution boards or MDBs serve as the central office of an electrical distribution system. This equipment is usually the first step inside the electrical energy white room. There is electricity from the primary power source, which distributes electricity to various sub-distribution boards or end circuits. High-capacity breakers with advanced protection features are often integrated within the MDB, which ensures the reliable flow of electricity and its management across large infrastructures.
The remaining power from an MDB is then circuit controlled by sub-distribution boards SDB, which serve as a secondary control point. The SDB is localized for control and protection. In multi-story office barrages, each floor could have an SDB to ease the thermic regulation of electricity. Efficiency on all levels with the other system board bases within the configuration Option, which type and configuration selected depend on the scale, load needs, and complexity of the electrical system. Irrespective of these conditions, both system boards are integral to efficiency m.
Resolution and Explanation of Commercial and Industrial Distribution Boards
In response to the query, commercial and industrial distribution boards are quite important for controlling and managing electrical distribution in larger facilities. These boards are specialized for more complex load and circuit requirements than what a typical household can handle. They have sophisticated circuit breaker systems and are sometimes equipped with monitoring devices to enhance safety, energy efficiency, and operational reliability for commercial and industrial purposes.
For example, modern industrial boards can accommodate heavy machinery and even the most advanced equipment because they support three-phase power systems. In addition, many of them have automated fault detection, load balancing metrics, and IoT capabilities for remote monitoring. With the development of innovative technologies integrated with sustainable energy, these boards can optimize the utilization of electricity resources, comply with regulations, and cater to other renewable sources of energy integration like solar or wind power. Customizable for diverse industries and applications, these boards are designed based on the facility’s needs.
Components of a Power Distribution Board
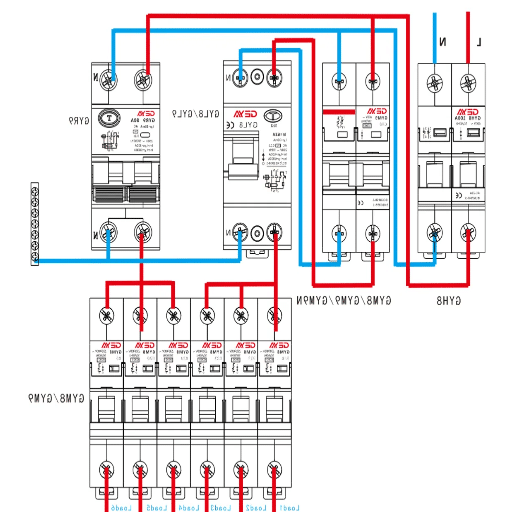
Essential Parts of a Distribution Board: Fuses, Breakers, and More
Electrical systems’ proper functioning relies on measuring several critical parts, which comprise a power distribution board. These are;
Fuses: These are called link fuses in terms of electrical engineering. Fuses stop the flow of current from the source when there is excessive current such that equipment will either overheat or sustain damage.
Circuit Breakers: A switch can usually be operated manually. However, breakers can switch on or off automatically. Breakers are protective circuitry that turns off the current being supplied in case a fault, such as a short circuit or overload, occurs.
Busbars: These gauges split into different parts or strips of metalwork, enabling even power disposition within the board’s different circuits.
Residual Current Devices (RCDs): These devices enhance a system’s degree of safety by first opening the power supply in case of an imbalanced electrical breakdown and then for bare leakage while either side is active.
Enclosure: The outer part that covers the main parts of a device is known as a shell. This robust case protects parts inside devices from any possible injury to the contour and user security.
Faulty devices cause electrical distribution system impairment. Each of these parts contributes greatly to the system’s security, functionality, and, more importantly, reliability and flexibility.
Working of Busbars and Terminal Blocks
Both busbars and terminal blocks play an essential role in electricity’s practical and systematic distribution into different circuits. Busbars are copper or aluminum conductive strips responsible for the central distribution of electricity to various parts of a system. They are solid and compact, reducing resistive loss and increasing their current carrying capacity. Because of their unique design, busbars have become the backbone of modern electrical systems. Typically, busbars are built to facilitate multiple connections at once, helping to increase efficiency while conserving space within a system.
Terminal blocks, in contrast, function as orderly connection interfaces for several wires, allowing for orderliness and ease of maintenance. Terminal blocks are highly regarded for their modular design, which permits rapid changes to a wiring configuration without complex processes. Their design also allows for ease of use, as terminal blocks often include protective features such as screw clamps or spring cages that prevent wires from being shaken loose by vibration or mechanical stress.
Together, busbars and terminal blocks increase the capabilities of complex electrical systems and facilitate easy and safe maintenance in residential, commercial, or industrial areas. They not only speed up processes like establishing or troubleshooting components but also guarantee functional reliability in tough conditions.
A Look at the Wiring and Encapsulation of an Electrical Distribution Panel
A distribution board’s wiring, including its enclosure, is critical for its safe and reliable operation. A single distribution board is divided into several circuits in an orderly fashion to power different areas or equipment. The wiring arrangement is done so that cables do not overlap or get tangled, which would predispose the wiring to short circuit risks and maintenance issues. During the installation and troubleshooting, colored cables for live, neutral, and grounding connections help enhance clarity.
The enclosure also has an essential function as a container and protector of the internal parts of the apparatus. Most modern enclosures are made from sturdy metals like steel and polycarbonate plastic, which can resist damaging impacts, bad weather, and fire. They include ventilation points to prevent overheating and blockable doors and transparent panels for convenient viewing without compromising security. These structures are rated with standard numbers for susceptibility to dust and water ingress, known as IP (Ingress Protection) rating, so their use is not limited to clean environments. The combination of a strong enclosure and superior wiring gives a fully serviceable and safe solution for electrical distribution.
How to Choose the Right Distribution Board for Your Needs?
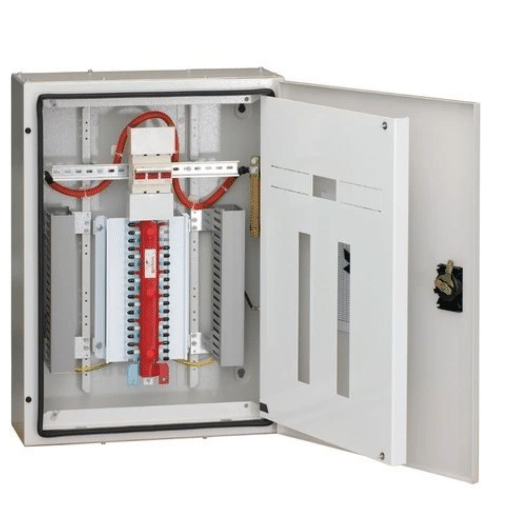
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Power Distribution Board
It’s essential to select an appropriate power distribution board for any project that requires electrical installation, as it makes the process safe, efficient, and reliable. In making your selection, consider the following:
Load Capacity and Demand: Look at the total demand and ensure that the board’s load capacity meets or exceeds your system’s requirements. This must also account for possible expansion needs in the future to prevent underloading or over-upgrades.
Type of Application: Clearly identify the type of board, i.e., whether it is for domestic, commercial, or industrial purposes. Each application has its own requirements, such as single-phase or three-phase systems.
Safety Features: Prioritize boards with protective features like circuit breakers, residual current devices (RCDs), and surprise protection features. These components reduce the risk of power surges, overloads, and short circuits.
Compliance with Standards: Always ensure that the distribution board meets local and international standard requirements, such as IEC 614392 or NEC regulations, when determining safety and quality compliance.
Ingress Protection (IP) Rating: Understand the different environments where the board is to be positioned. The higher the IP rating, the greater the protection provided, making it ideal for dusty, wet, or outdoor locations.
Material and Durability: Ensure the boards you want to purchase are made from rigid materials, such as metals or durable plastics. The fireproof and corrosion-proof enclosures aid in the longevity and safety of the equipment.
Flexibility and Scalability: Select a board with a modular design that leaves enough room for spare circuits. This is advantageous for installation and future upgrade modifications.
Aesthetic and Compact Design: For home or office use, the distribution board’s aesthetic features and compactness are important so that it blends with the surroundings without taking up too much space.
Now, with these criteria carefully evaluated, you can make a favorable choice toward a distribution board that will respond to your requirements and guarantee a dependable and safe electrical system for years to come.
The Significance of Voltage Ratings: Differences Between AC and DC Power Supplies
All electrical systems are designed considering voltage ratings as they have a vital impact on safety, efficiency, and compatibility with AC and DC power supplies. Regarding AC systems, voltage ratings for residential use are usually between 120V and 240V, whereas industrial applications might require higher voltages from several kilovolts. Following voltage ratings minimizes the chances of insulation failure as well as overheating. DC systems used to power battery-operated devices like mobile phones or renewable energy systems also need accurate voltage levels to be set, mainly if the system contains highly sensitive electronics to avoid damage and ensure proper functionality.
Renewable energy systems and enhanced energy storage capabilities have put even greater emphasis on the requirement of voltage compatibility. Contemporary solar power systems use DC inputs while employing inverters to change electricity into AC for normal use due to the need for a match in the voltage range. There is also a shift in the industry towards using high-power, high-voltage DC (HVDC) transmission due to greater efficiency in transmitting power across long distances at lower energy loss than AC systems.
This thoughtful observation of voltage ratings directly contributes to reliable operation while improving longevity, reducing energy waste, and enabling the use of energy-efficient technologies across residential and industrial sectors.
Evaluating Electrical Load Requirements for the Distribution Panel
Evaluating electrical load requirements is one of the most critical steps in assuring the distribution panel will operate safely and efficiently. This process starts with determining power demand, which entails summating the wattage of all electrical devices and appliances. This usually includes lighting, HVAC equipment, modern refrigerators, and other essential electronics for homes. Industrial settings may also require consideration of specific machinery, motors, and tools.
One important item to consider is peak load, which depicts the electricity consumption at a given time during high demand. It is essential that this load be accommodated without exceeding the panel’s capabilities; otherwise, overheating and electrical problems may arise. In addition, there is always a need to consider expansion possibilities, say, new circuits or new appliances that will need to be added later on, which is why additional capacity is required.
Another important step in preventing an overload of certain breakers is balancing the load across different circuits. This improves system reliability and maintains the proper power distribution within the system. Load calculators or consulting professionals can help perform the appropriate load analysis to aid in meeting the compliance objectives. In the end, adopting a methodical approach to load evaluation maximizes the responsive capacity of the distribution panel so that greater energy efficiency and more advanced electrical technologies are seamlessly integrated.
Maintenance and Safety Tips for Distribution Boards

Routine Checks and Maintenance Practices for Electrical Safety
Routine checks are crucial to maintaining the integrity and safety of distribution boards and lowering the risks of electrical failures and hazards. An important step is to check circuit breakers and protective devices for any signs of wear, overload, or thermal damage. A loose connection requires lessening the box’s tightness, but a loose connection can lead to arcing and/or overheating problems in the long run.
Regular thermal imaging scans can also be used to check for hotspots that might indicate overworked circuits or some other component that is not functioning correctly. Cleaning the distribution board occasionally to remove moisture, debris, and dust is an important maintenance step because these ions can cause short circuits and corrosion.
Additionally, systems like RCDs should be tested at predetermined time intervals to ensure proper functioning, that is, tripping during fault conditions. A complete log of all maintenance activity, inspections, or any other actions, such as replacements and repairs, should also be kept to allow easier tracing of the problem later and make it more accountable.
When users adopt some of these measures, they can reduce downtime, improve system performance, and comply with existing electrical safety and code regulations. Proper maintenance is not only preventative but, rather, an investment in system reliability and safety for the long term.
How to Identify Problems with Your Distribution Board
An inspection routine for your distribution board is essential to improve safety and ensure you do not lose electricity. Some visual indicators include scorch disfigurements, discoloration, and wear of wires and breakers that suggest overheating or loosened connections. Sounds like buzzing or crackling may also suggest lurking electrical issues that need resolution.
Pay close attention to breakers that trip frequently, which may indicate overloaded circuits or fault conditions. Power delivery is another case in which people should check power delivery consistency, for example, dimming or flickering lights. Also, keep an eye on the overall temperature of the distribution board; if it is warm or hot, that is.
Tools such as multimeters and infrared thermometers can help to detect anomalies like voltage fluctuations and hotspots. It is also necessary to analyze load distribution across the circuits to confirm that the system is not overloaded. If you are unsure, seek the advice of a licensed electrician who can conduct a proper evaluation to remain within safety regulations and limit potential dangers.
Best Practices for Operating a Distribution Panel Safely
Identify Parts and Their Marking
Study the design of each distribution panel before working on it. Each panel has a label that stipulates the different circuits, making it easy to locate certain breakers. Knowing these components facilitates smooth functioning and minimizes errors.
Perform Periodic Checks
Diagnostics are carried out to check for signs of deterioration, loose fittings, or an increase in temperature. Slowly looser arcs and inadequate terminal tightening can lead to arcing and fire hazards. Infrared thermometers are reliable for finding hotspots. Make sure you keep notes of your visits to ensure measurement for compliance.
Use the Right Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Exposed electrical panels can lead to electrical arcing and shocks. Incidents like these require the use of insulated gloves, safety goggles, and clothing that can withstand fire to reduce risk when dealing with energized panels or troubleshooting.
Observe Load Management Directions
Alteration of systems can also alter the functioning of the distribution panels. If load capacity is exceeded, tripped breakers, overheating, and faulty components are usually the results. To ensure safety and efficiency, the efficiency of each circuit should be assessed regularly by calculating the total load.
Following The Safety Precautions Procedures
Before performing maintenance on a unit, due diligence is exercised by ensuring that a panel is de-energized using a LOTO device. When used correctly, LOTO devices/tags prevent equipment and personnel from being harmed by unexpected re-energization.
Keep all records updated on time
Update the panel’s schematics and operational logs. Save all modifications, repairs, or testing activities to set a reference for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Act on Alarms and Signals in a Timely Fashion
Some advanced monitoring systems of modern distribution panels may contain response monitoring features such as alarm indicator lights for too much current or a broken circuit. These signals should be escalated to the highest priority for attention to avoid turning into other costly or hazardous failure modes.
Ensure the area near the panel is clean and secured
To maintain reliable operation over time, the components of the panel need protection. Moisture, dust, and other obstructions should be kept from the distribution panel and its surroundings.
It is strongly advised that you always take safety measures and speak to a professional for more complex issues. These best practices will get you closer to ensuring the efficient operation of a distribution panel and mitigating unexpected risks and downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is a distribution board in an electrical circuit?
A: A distribution board is a panelboard or consumer unit and an important part of the electrical circuit where power is distributed. It is the point of division between the main power system and the auxiliary electrical circuits. It also serves as the central point, receiver of circuit protection, and controlling unit for the safe and efficient use of electrical power within the system.
Q: How does a distribution board protect against overcurrent?
A: A distribution board incorporates circuit breakers or fuses as protective devices to avert overcurrent flow at the output terminals. These devices automatically disconnect the circuit whenever the current drawn out exceeds the rated one to prevent harmful damages, such as short-circuit hazards.
Q: What is the difference between a fuse box and a breaker panel?
A: A fuse box incorporates fuses that one has to replace once they are blown. On the contrary, a breaker panel or distribution board houses circuit breakers that can be turned back on once they are tripped. In modern Electrical supply Systems, fuse boxes are being replaced by fuse panels as they are more convenient and safer to use.
Q: What purpose does the main switch serve in a distribution board?
A: The main switch in a distribution board, otherwise known as the ‘main breaker,’ is responsible for the total electricity supply system to the board. It enables a consumer of electricity to turn off all circuits simultaneously, which serves as a safety system when the electrical system is being maintained or in an emergency situation.
Q: Can a single distribution board utilize AC and DC voltages?
A: Distribution boards are generally designed for AC voltage, which applies to practically every home and business electrical system. However, some special distribution boards can also be made for DC voltage, especially in renewable energy systems such as solar power installations.
Q: Which components are ordinarily present inside a distribution board?
A: A distribution board normally contains circuit breakers, a main switch, busbars, and sometimes a power meter for measuring the amount of electrical energy consumed. All these parts interact and share the need to distribute electrical power safely to several circuits in a building.
Q: Can you describe a busbar and explain its role in the distribution board?
A: A busbar is a conductive component, usually composed of copper or aluminum, that integrates and delivers power in a distribution board. It acts like a hub for many connections, enabling power flow to numerous circuit breakers or fuses.
Q: Why does power quality matter in an electrical circuit?
A: Devices violate their design criteria when the quality of the power consumed through the distribution board is less than desirable. Quality issues can result in breakdowns, reduced efficiency, and excessive deterioration of machines. Monitor and maintain the circuits to ensure correct protection and restrict high-quality electric power.
Q: What should I take when the circuit breaker keeps tripping from the distribution board?
A: A tripped circuit breaker indicates that there may be the possibility of too much current draw because of an overloaded circuit, short circuit, or faulted wiring. Seek the assistance of a competent electrician to evaluate the situation and carry out the necessary repair work to guarantee the electrical circuit meets safe operating standards.







